What is MemOS?
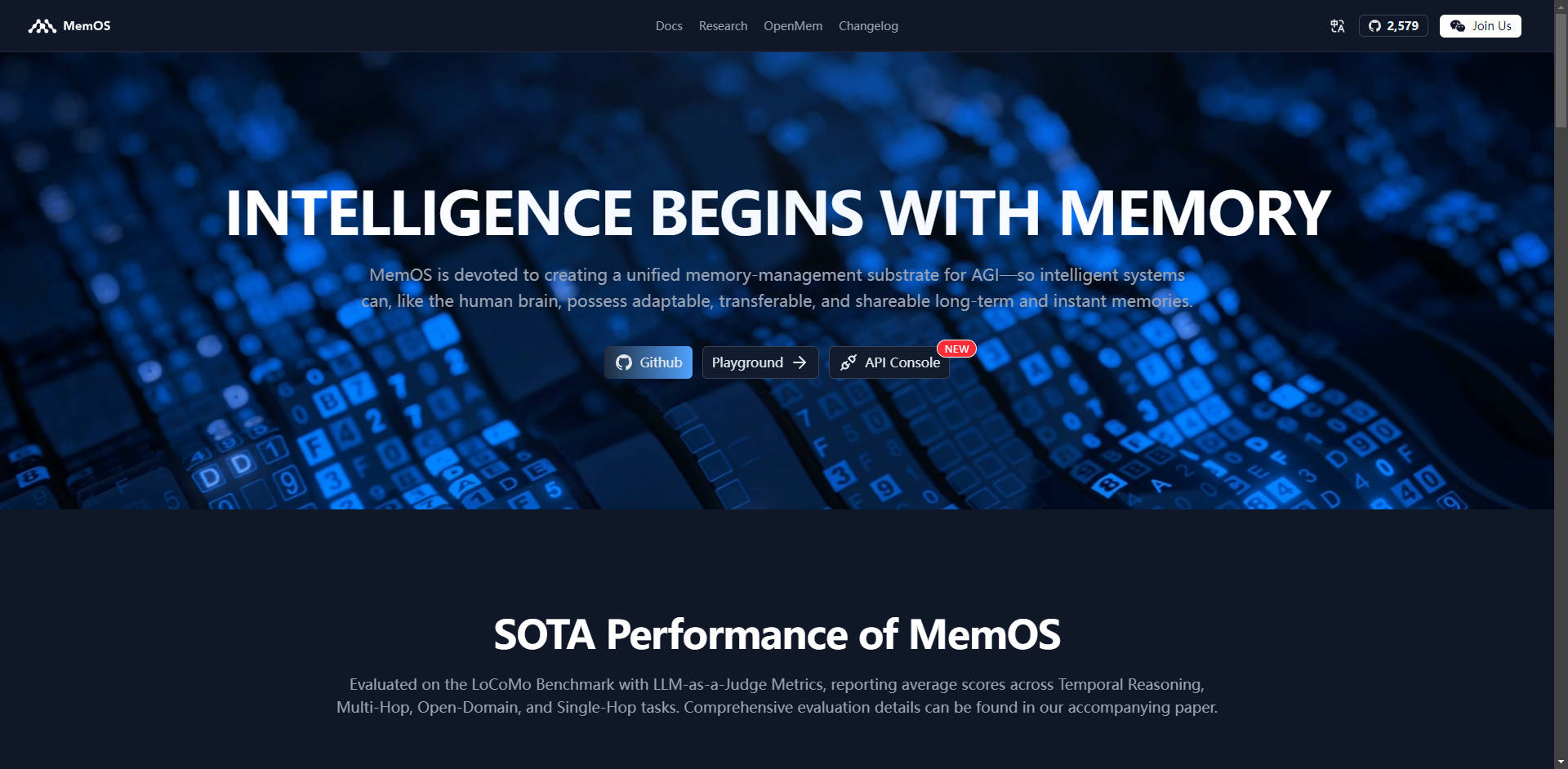
Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with persistence, limiting their ability to retain context and evolve beyond a single session or prompt window. MemOS (Memory Operating System) is an industrial-grade, open-source framework designed to solve this critical challenge. By treating memory as a first-class system resource, MemOS provides LLMs with structured, persistent, and transferable long-term memory, transforming them from static generators into adaptive, continuously learning digital assistants.
Key Features
MemOS adopts a layered architecture, drawing inspiration from traditional operating systems, to provide a comprehensive, systematic approach to AI memory management.
🧠 Standardized MemCube Unification
MemOS introduces the MemCube, a standardized encapsulation that organically integrates three distinct types of memory: plaintext memory (context/dialogue history), activation memory (KV Cache and intermediate states), and parameter memory (long-term knowledge and fine-tuning data). This unified framework allows models to retrieve, update, and compose memory dynamically, supporting more accurate reasoning and adaptive behaviors across tasks.
🚀 Predictive Memory Scheduling
Instead of waiting for memory retrieval, MemOS employs a novel Memory Scheduling paradigm featuring Next-Scene Prediction. Based on contextual cues and task intent, the scheduler asynchronously forecasts potential memory needs and preloads relevant memory fragments into the working context. This significantly reduces response latency, optimizes GPU utilization, and ensures highly efficient, context-aware memory access.
🔗 Standardized Memory API and Interoperability
The system provides a standardized Memory API for developers, enabling seamless integration of persistent memory operations (creation, update, transfer, rollback) into LLM workflows. This layer supports cross-model and cross-session memory transfer, allowing intelligent systems to share and reuse context and knowledge across different agents, devices, and applications.
Use Cases
MemOS enables the development of complex, long-term AI applications that require continuity, reliability, and personalization.
Personalized Digital Agents: Build true long-term digital assistants that continuously accumulate user preferences, historical interactions, and behavioral habits. Each subsequent interaction leverages a deeper, evolving memory base, leading to highly personalized and relevant service that improves over time.
Structured Research and Knowledge Management: For research teams or enterprises, MemOS allows for the structured, long-term preservation of dispersed project data, analysis results, and notes. Researchers can deploy intelligent assistants capable of dynamic, multi-hop retrieval across a vast, continuously updated knowledge base, ensuring research continuity and high efficiency.
High-Reliability and Auditable Systems: In fields like finance or law, where traceability and compliance are paramount, MemOS provides memory provenance and auditing functions. Model inferences can be precisely traced back to the specific knowledge source within the memory system, significantly enhancing transparency, auditability, and overall system trustworthiness.
Unique Advantages
MemOS provides verifiable performance gains and architectural stability that distinguish it from traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) or basic caching solutions.
1. State-of-the-Art Performance in Long-Term Reasoning
Evaluated on the industry-recognized LoCoMo (Long Conversational Memory) Benchmark, MemOS demonstrates superior performance across complex memory tasks:
| Task Category | MemOS Score | OpenAI Global Memory | Improvement vs. OpenAI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temporal Reasoning | 73.21% | 28.25% | +159% |
| Multi-Hop Retrieval | 64.30% | 60.28% | +6.7% |
| Open Domain | 55.21% | 32.99% | +67.3% |
| Single Hop | 78.44% | 61.83% | +26.8% |
| Overall Accuracy | 73.31% | 52.75% | +38.97% |
MemOS's substantial lead in Temporal Reasoning—the task requiring the highest system demands—validates the efficiency and accuracy of its unified memory scheduling and retrieval mechanisms in complex, long-context scenarios.
2. Enhanced Efficiency and Token Savings
The predictive scheduling and optimized retrieval framework allow MemOS to achieve high accuracy using significantly less context length.
MemOS achieves optimal performance using approximately 1,000 tokens of context length (Top-K 20).
Comparative systems often require 2,000–4,000 tokens to reach similar accuracy levels.
By minimizing the required input size for accurate recall, MemOS drastically reduces encoding cost, lowers computational burden, and improves overall system throughput.
3. Accelerated Inference via KV Cache Reuse
MemOS efficiently manages and reuses Activation Memory (KV Cache) in scheduling scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that as model size and cache context length increase, the time-to-first-token (TTFT) acceleration ratio increases significantly. In long-memory scenarios, the TTFT acceleration ratio exceeds 70%, proving the value of the memory scheduling layer for enhancing decoding performance and overall responsiveness in large-scale inference tasks.
Conclusion
MemOS provides the essential foundation for building intelligent systems that truly remember, adapt, and evolve. By offering a standardized, industrial-grade framework for unified memory management and predictive scheduling, MemOS enables developers and enterprises to unlock new levels of intelligence, reliability, and efficiency in their LLM applications.
Explore the future of intelligent systems: Learn more about MemOS on GitHub or sign up for the upcoming Playground feature to see the performance gains firsthand.
More information on MemOS
Top 5 Countries
Traffic Sources
MemOS Alternatives
Load more Alternatives-

-
-
OpenMemory: The self-hosted AI memory engine. Overcome LLM context limits with persistent, structured, private, and explainable long-term recall.
-
Agents promote human-type reasoning and are a great advancement towards building AGI and understanding ourselves as humans. Memory is a key component of how humans approach tasks and should be weighted the same when building AI agents. memary emulates human memory to advance these agents.
-